Management and Organizational Structure in Today’s Market
-
 Mareem Kadhim
Mareem Kadhim - 13 May, 2024
Management and Organizations Structure in Today’s Market
Understanding the Fundamentals of Project Management: A Comprehensive Guide
Projects are integral to every aspect of life; in fact, we can say “Life is a project.” Whether in work, careers, or personal endeavors, understanding the various levels of project management is crucial for achieving success. This guide will explain key project management terminology and concepts, illustrated with examples for clarity.
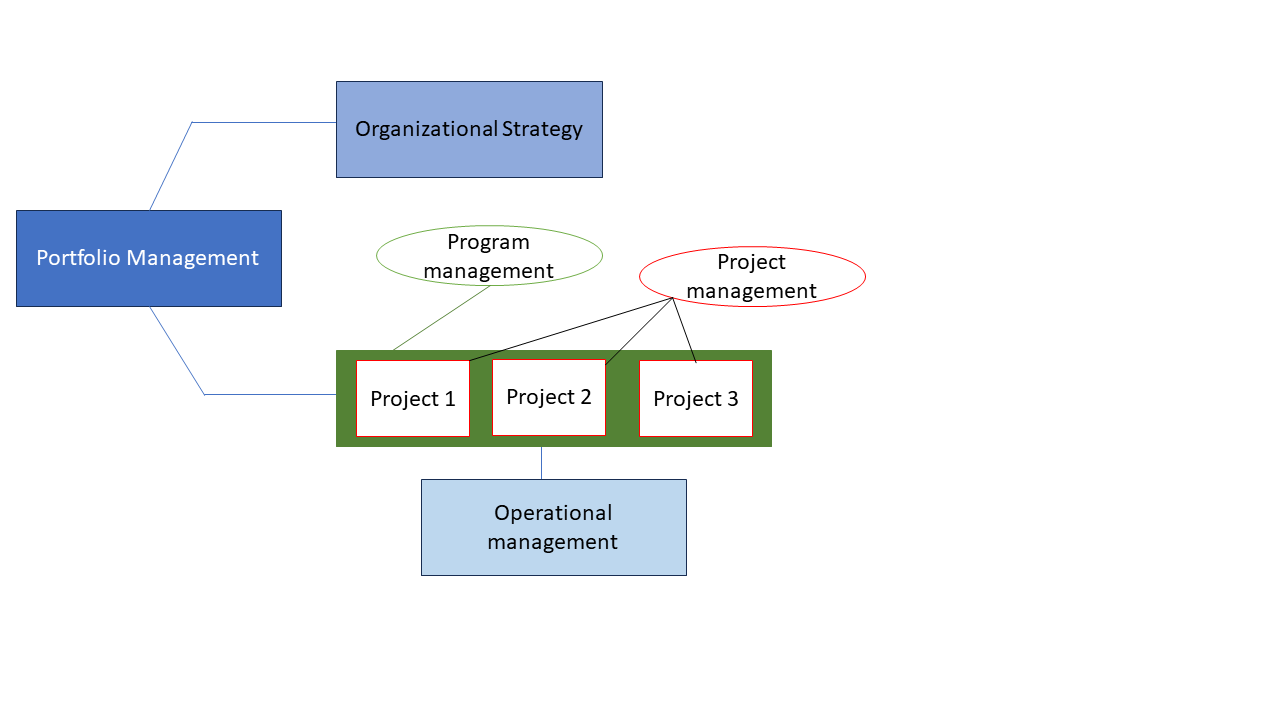
Portfolio Management: Aligning Strategies with Operations
Portfolio management involves overseeing a collection of projects and programs to ensure they align with the organization’s strategic objectives. It encompasses all types of management and operations within an organization.
Example: A large multinational corporation operates in multiple industries, each with its own set of projects and initiatives. Portfolio management helps the organization prioritize and align these projects with its strategic objectives. For instance, if the company’s goal is to expand into new markets, portfolio management identifies and prioritizes projects related to market research, product development, and market entry strategies, ensuring resources are allocated effectively.
Benefits:
- Optimizes resource allocation
- Mitigates risks
- Ensures projects contribute to overall business goals
Program Management: Facilitating Coordination and Alignment
Program management focuses on managing a set of related projects under a specific portfolio, ensuring their interdependencies are managed effectively.
Example: A software company is developing a new suite of products requiring coordination across multiple projects, including software development, hardware integration, and marketing campaigns. Program management provides a centralized framework for planning, communication, and decision-making. Program managers oversee project interdependencies, identify risks, and implement strategies to address them proactively.
Benefits:
- Enhances coordination and alignment between projects
- Identifies and mitigates risks and issues
- Ensures projects support the overall program objectives
Project Management: Ensuring Efficient Execution
Project management is the application of skills, knowledge, and tools to meet specific project requirements.
Example: A construction company is tasked with building a new office complex within a tight timeline and budget. Project management ensures the project is executed efficiently and meets client requirements. Project managers coordinate activities such as site preparation, construction, procurement, and quality assurance, while managing resources, schedules, and budgets. Techniques like critical path analysis help identify critical tasks and allocate resources to minimize delays.
Benefits:
- Delivers projects on time and within budget
- Meets specifications and quality standards
- Ensures safety and efficiency
Operational Management: Transforming Resources into Products and Services
Operational management involves transforming resources or data into services or products, managed by organizational strategy managers.
Example: A retail chain operates multiple stores across different locations, each handling daily operations such as sales, inventory management, customer service, and staffing. Operational management ensures these activities are efficiently executed, delivering a seamless shopping experience for customers while maximizing profitability.
Benefits:
- Improves efficiency in daily operations
- Enhances customer experience
- Maximizes profitability
Project Management Terminology
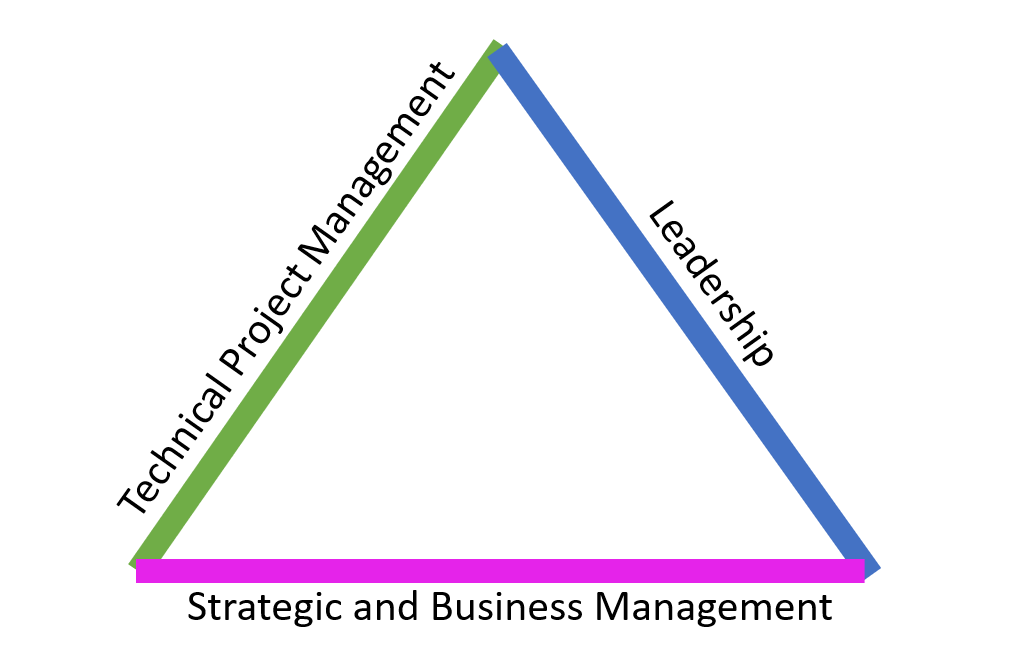
Mastering the PMI Talent Triangle for Project Management Success
If you have pursued the Project Management Professional (PMP) designation, you have likely encountered the PMI Talent Triangle. This framework represents the three key skill areas that project management professionals must develop to succeed in their careers. Based on extensive research and feedback from industry experts, the Project Management Institute (PMI) defines these essential components as follows:
Project Management Institute Talent Triangle
1. Technical Project Management
Technical Project Management encompasses the knowledge, skills, and techniques required to manage projects effectively. This includes understanding project management processes, methodologies, tools, and techniques, and applying best practices to ensure projects are delivered on time, within budget, and according to scope.
** Key Aspects:**
- Mastery of project management software and tools
- Proficiency in methodologies such as Agile, Waterfall, or Hybrid
- Expertise in project planning, scheduling, and risk management
** Benefits:**
- Ensures consistent delivery of project goals
- Enhances efficiency and accuracy in project execution
- Improves risk mitigation and problem-solving capabilities
2. Leadership
Leadership skills are crucial for project managers to inspire and motivate team members, build strong relationships, communicate effectively, and drive project success. Effective leadership involves qualities such as vision, communication, conflict resolution, negotiation, and decision-making.
** Key Aspects:**
- Inspiring and motivating teams
- Building and maintaining stakeholder relationships
- Effective communication and conflict resolution
- Strategic decision-making and problem-solving
** Benefits:**
- Fosters a collaborative and productive project environment
- Enhances team cohesion and morale
- Drives successful project outcomes through effective team management
3. Strategic and Business Management
Strategic and Business Management focuses on aligning projects with organizational goals and objectives. This includes understanding business strategy, making strategic decisions, analyzing market trends, identifying opportunities, managing risks, and ensuring projects deliver value to stakeholders.
** Key Aspects:**
- Aligning projects with business goals
- Strategic decision-making
- Market trend analysis and opportunity identification
- Risk management and value delivery
** Benefits:**
- Ensures projects contribute to overall business success
- Enhances the strategic value of project outcomes
- Improves risk management and opportunity exploitation
Why Master the PMI Talent Triangle?
By developing proficiency in these three areas—technical project management, leadership, and strategic and business management—project management professionals can significantly enhance their effectiveness. Mastery of these skills leads to career advancement and greater value delivery to organizations.
The PMI Talent Triangle serves as a comprehensive framework for guiding professional development, ensuring project managers possess a well-rounded expertise that enables them to navigate the complexities of modern project environments successfully.
Embracing the PMI Talent Triangle equips project management professionals with a balanced skill set that is essential for driving project success. Whether you are advancing in your career or striving to deliver exceptional value to your organization, focusing on technical skills, leadership, and strategic business management will set you on the path to excellence in project management.
By consistently developing these areas, you can navigate the complexities of any project with confidence, ensuring successful outcomes and contributing to your organization’s strategic goals.
What Affects a Project?
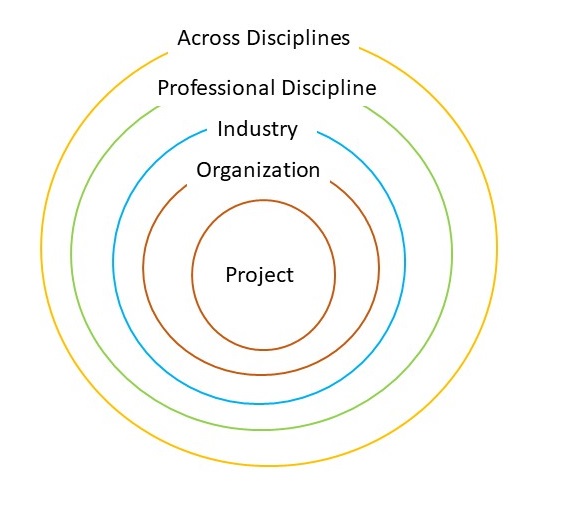
Project’s Sphere of Influence
In the realm of project management, the concept of ‘Sphere of Influence’ holds significant importance. This terminology describes a field or area in which an individual, such as a project manager, possesses the power to affect events and outcomes. Within this sphere, project management professionals take on various roles that reflect their capabilities and embody the values they bring to the table. For example, they may serve as leaders, facilitators, or decision-makers, utilizing their expertise and experience to drive projects forward and achieve desired objectives. By understanding their roles within the sphere of influence, project management professionals can leverage their capabilities and contributions to effectively navigate challenges and steer projects toward success.
Understanding Organizational Structures: A Guide for Business Success
Organizational structures play a pivotal role in defining how responsibilities are distributed among different entities within a company. These structures are not one-size-fits-all; they vary based on the company’s objectives, strategies, and industry dynamics. Various factors shape organizational structures, including alignment with organizational goals, specialized capabilities, span of control, efficiency, effectiveness, and clarity in decision-making processes.
Common Types of Organizational Structures
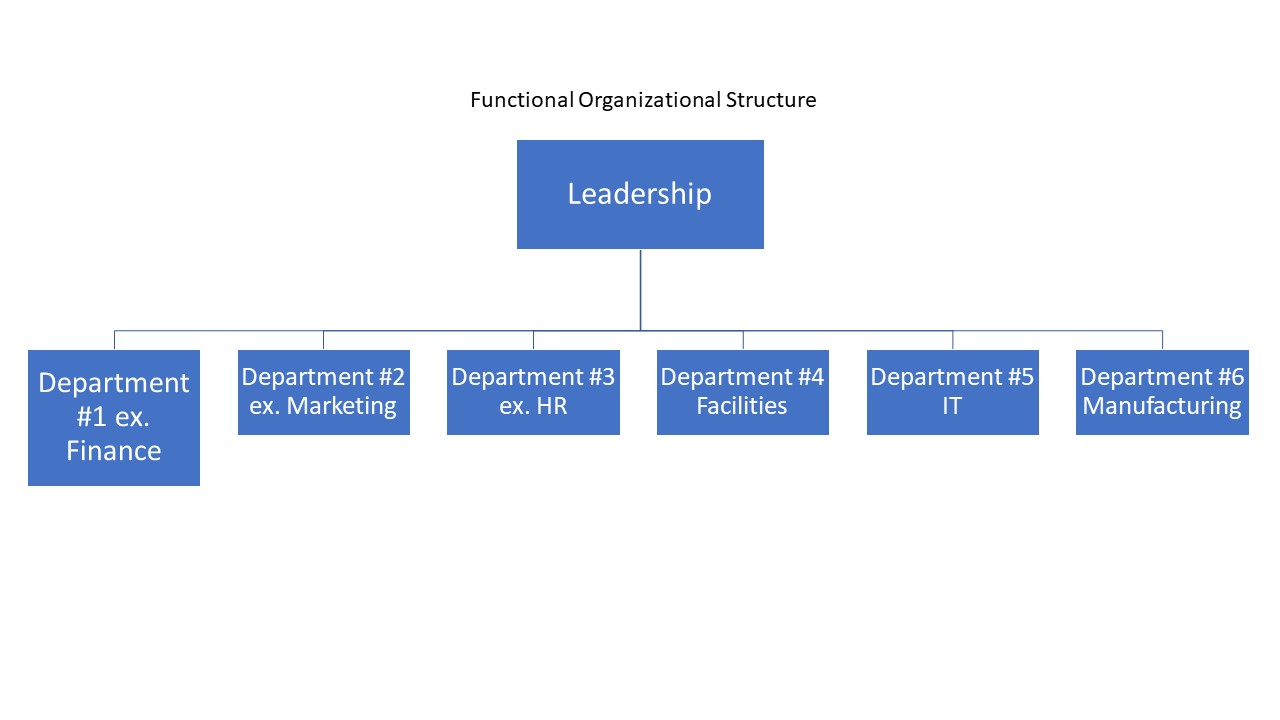
1. Functional Structure
This type of structure groups employees based on specialized functions or roles, such as engineering, marketing, and finance. Each functional area operates independently, reporting to a centralized authority like a department head or manager.
** Example:**
Google employs a functional organizational structure, where employees are organized based on their specialized functions. This approach is common in large, established companies like Google, facilitating focused expertise and efficiency within each functional area.
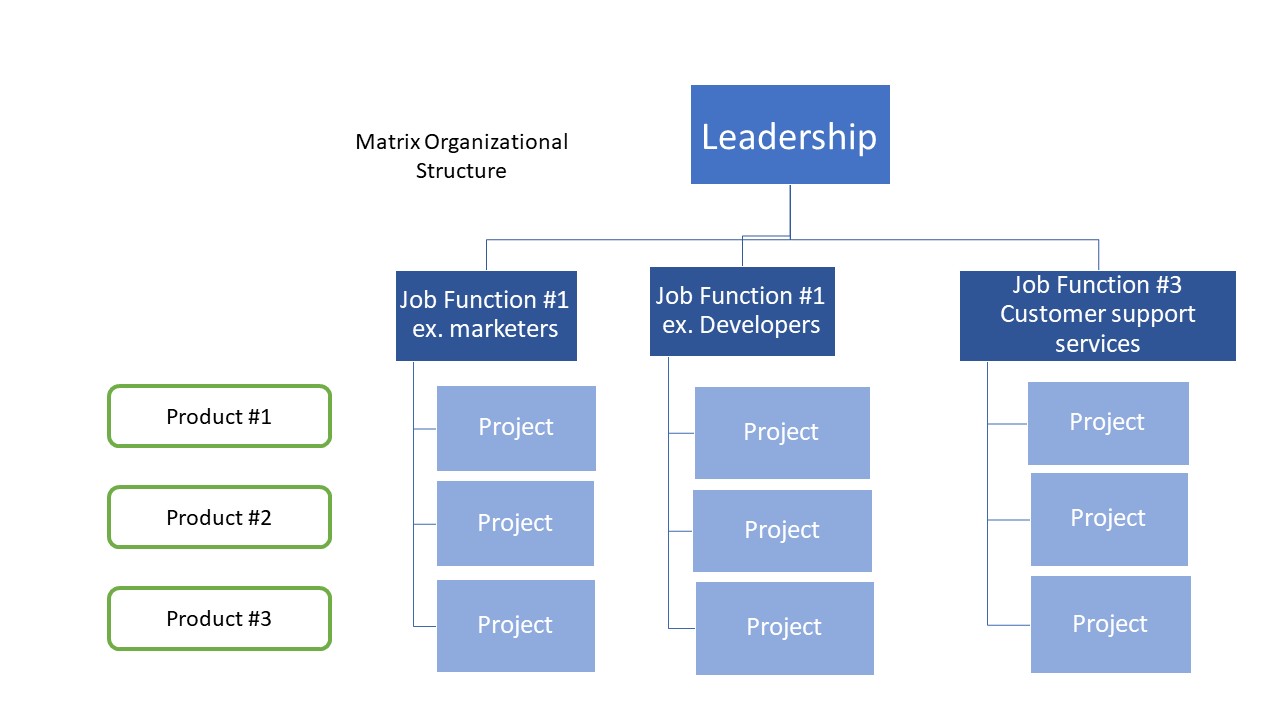
2. Matrix Structure
In a matrix structure, functional and divisional structures are combined to support a diverse product range or complex projects. Employees report to both functional managers and project managers, creating dual lines of authority.
** Example:**
OpenText utilizes a matrix organizational structure to support its diverse range of products and services. This structure allows for flexibility and adaptability, as employees collaborate across functional lines to support various projects and initiatives.
Why Understanding Organizational Structures Matters
By grasping the nuances of organizational structures, businesses can optimize their operations, enhance communication, and foster innovation. Understanding how different structures function enables companies to tailor their approach to suit their unique needs and objectives. Whether it’s streamlining processes, fostering collaboration, or adapting to market changes, a well-designed organizational structure lays the foundation for business success.
Optimizing Organizational Structures for Success
Effective organizational structures are essential for business success. By optimizing your organization’s structure to align with your goals and industry dynamics, you can enhance efficiency, foster innovation, and drive growth. Whether it’s adopting a functional, matrix, or hybrid structure, choosing the right approach can propel your business forward and position it for long-term success.
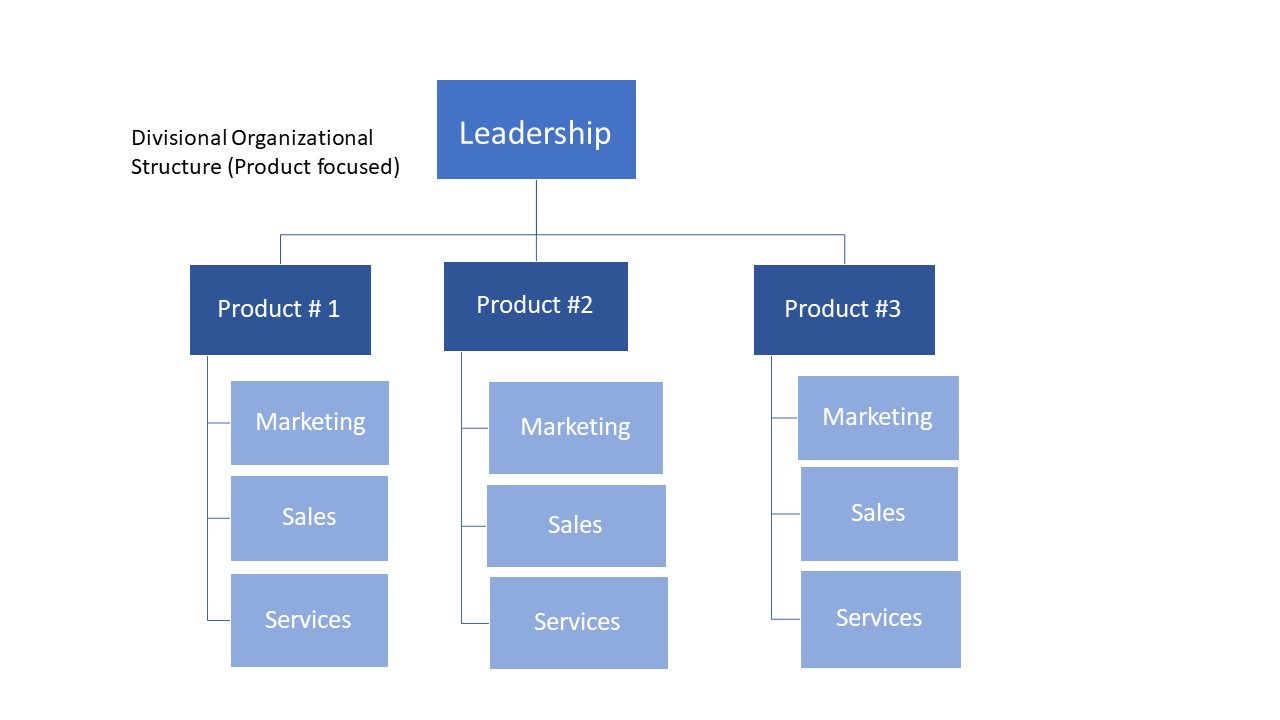
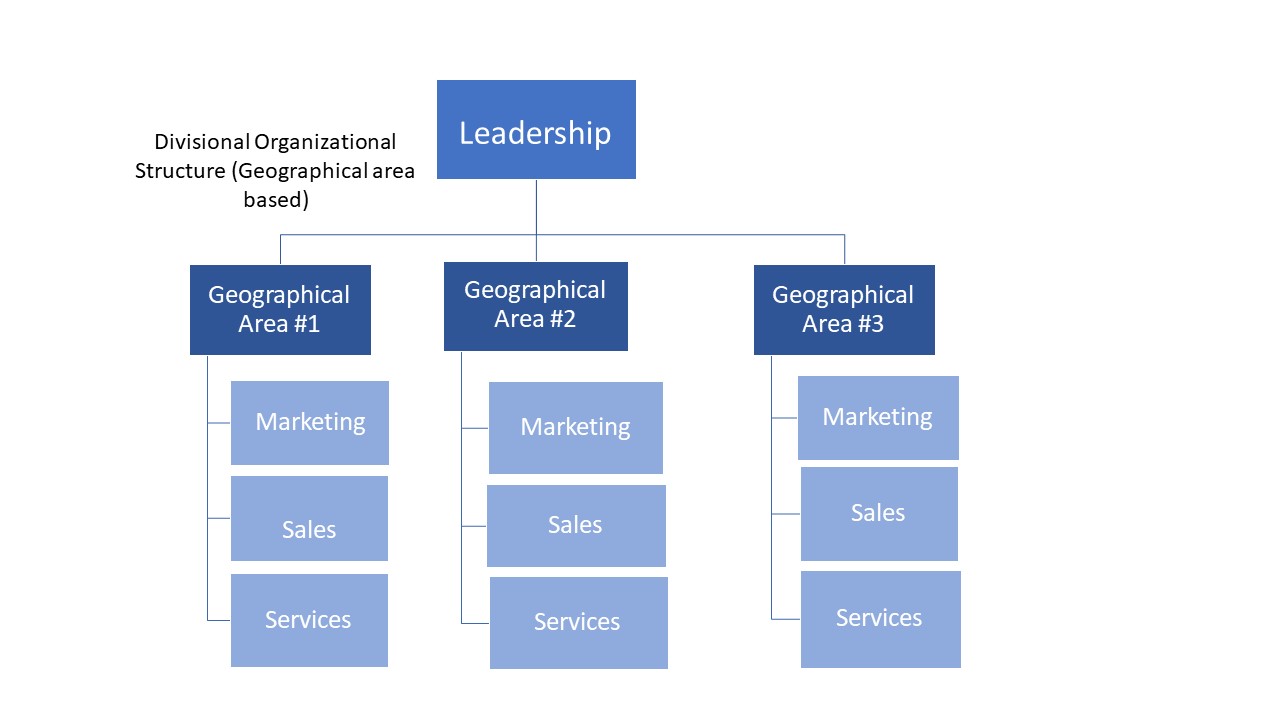
According to Forbes Advisor, organizational structures are commonly classified into four popular types, which will be illustrated in the following /images:
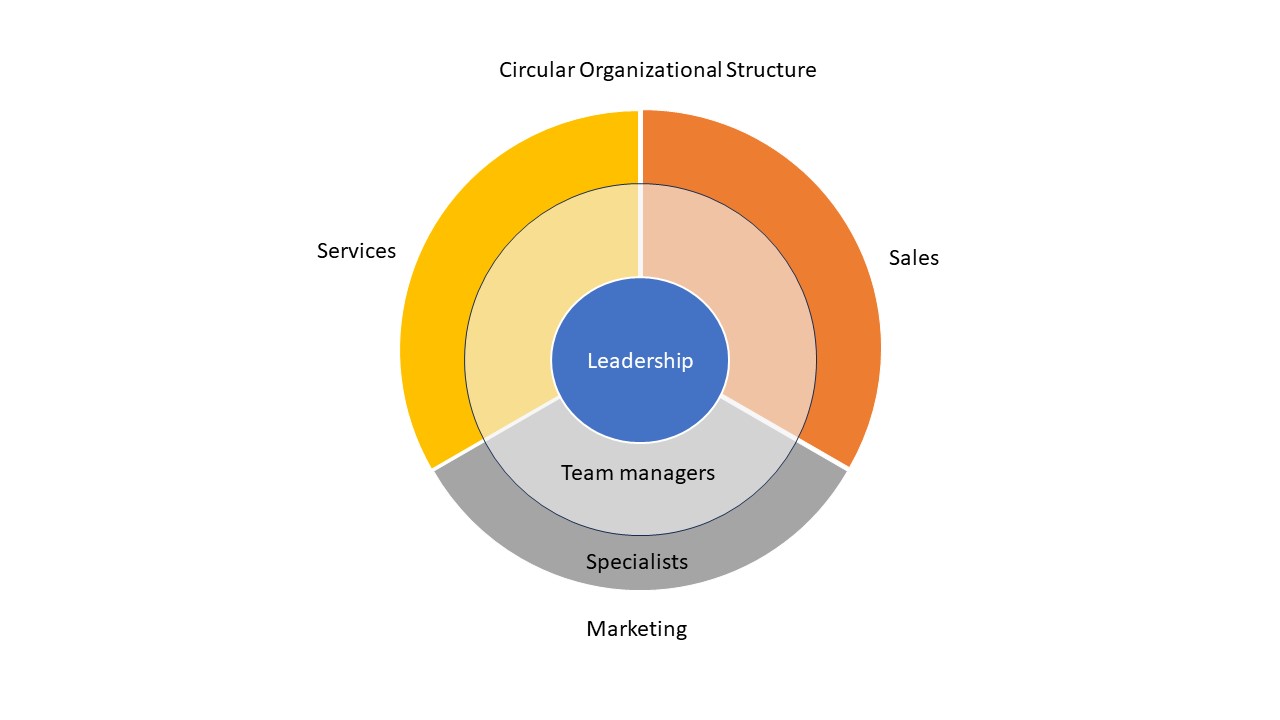
Most common type of organizational structure “functional”
Organizational structures serve as the backbone of any company, shaping how tasks are delegated, decisions are made, and resources are allocated. By understanding the various types of organizational structures and their implications, businesses can navigate complexities more effectively, drive efficiency, and achieve strategic objectives. Embracing a flexible and adaptive approach to organizational design empowers companies to thrive in dynamic and competitive environments.
How To Choose the Best Organizational Structure
Choosing the Right Organizational Structure: A Comprehensive Guide Selecting the most suitable organizational structure for your company is a crucial decision that requires careful consideration of several key factors. Here’s a detailed overview of what you need to take into account:
1. Current Roles and Teams
Assess the existing organization of job functions and teams within your company. Determine whether the current structure promotes effective communication, collaboration, and productivity, or if it hinders employee growth and innovation. Identify areas where improvements can be made to better align roles and responsibilities with the company’s objectives and strategic initiatives.
2. Strategic Plan
Align the choice of organizational structure with your company’s strategic goals and objectives, both in the short-term and long-term. Consider how different structures can support your business strategies and contribute to achieving desired outcomes. Evaluate whether the proposed structure enables flexibility and scalability to adapt to future changes and challenges.
3. Feedback from Stakeholders
Solicit feedback from employees, leadership, and other stakeholders within your organization. Listen to their perspectives on how the current organizational structure impacts their work, collaboration, and overall effectiveness. Additionally, gather input from external stakeholders such as customers and suppliers to understand how the structure affects their interactions with your company. Use this feedback to identify areas for improvement and inform your decision-making process.
4. Alignment
Ensure that the chosen organizational structure aligns with your strategic plans and addresses any feedback received from stakeholders. Strive to create a structure that facilitates effective communication, collaboration, and decision-making, while also supporting the achievement of your company’s goals and objectives. Seek alignment between the organizational structure and the company culture to promote employee engagement and satisfaction. By carefully considering these factors and evaluating how different organizational structures align with your company’s needs and objectives, you can make an informed decision on the best structure to support your organization’s success. Remember that organizational structures are not static and may evolve over time as your company grows and adapts to changing market conditions and business requirements.
In Conclusion, choosing the right organizational structure is a critical step in setting your company up for success. By considering factors such as current roles and teams, strategic alignment, stakeholder feedback, and overall alignment, you can make an informed decision that supports your company’s growth and long-term goals. Keep an open mind, remain flexible, and be prepared to adapt your structure as needed to meet the evolving needs of your business.